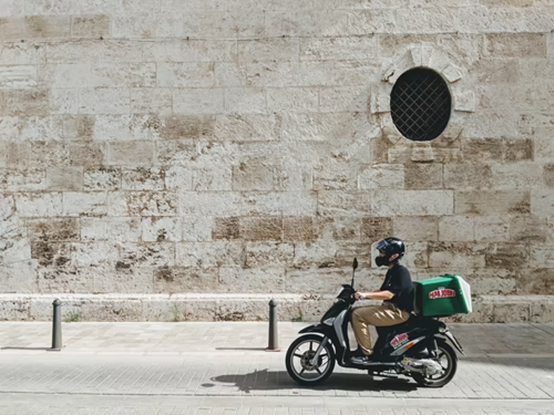
For those unfamiliar, the ‘last mile problem’ is a challenge that businesses of all types face every day. In telecom, It’s a phrase that refers to the final leg of communication networks delivering connectivity to retail customers–the last 20% of the overall network fabric that actually reaches the end-user.
What is Last-Mile Delivery?
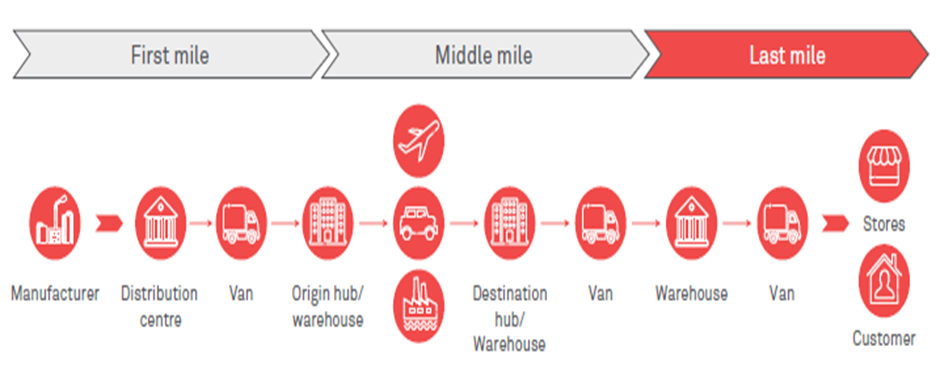
Last-mile delivery is the process of conveying packaged items from a courier company’s warehouse to the buyer’s location. The above image clearly shows the entire delivery cycle of an order.
Problems in Last-Mile Delivery
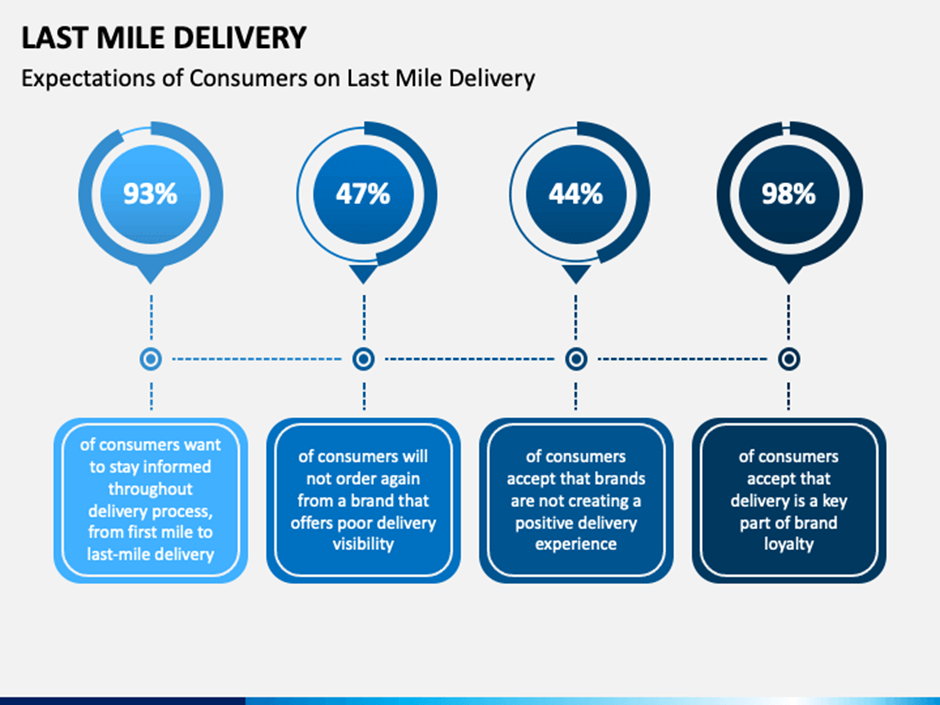
The above chart is a simplified depiction of what expectations a customer has on the last mile delivery of the order. It is therefore important to keep track of things and ensure that there is no fault in our last-mile delivery procedure. Below are some of the last-mile delivery challenges which all logistic companies should take care of.
Executing Same Day Delivery or on-time delivery: According to studies, more than 80% of customers currently are prepared to pay extra for faster delivery, and meeting this expectation is the most difficult obstacle for last-mile deliveries. Reduced delivery turnaround times are exceedingly difficult to achieve due to inefficient routing systems, human dependence on distributing work, and poor third-party logistics provider management, posing a risk to the entire shipping process. Another problem is ensuring that all of the vehicle’s capacity is utilized. Due to the fact that same-day deliveries sometimes consist of little products, fully using truck capacity is challenging, putting a dent in a logistics company’s massive savings. Businesses cannot afford to wait for enough orders to arrive to ensure that their capacity is fully used.
Traditional Routing Models: Without highly efficient routing systems and methods, ensuring timely and cost-effective execution of last-mile deliveries is challenging, if not impossible. Traditional routing models are mainly reliant on manual methods, making it impossible to consider all of the factors that influence the design of highly productive routes. With manual routing procedures in place, modifying a route based on real-time variables like weather, traffic congestion, unexpected road closures, unintended detours, and more is a significant issue, delaying the delivery process.
Poor Logistics Visibility: Inadequate visibility of logistics operations is a primary cause of time-consuming procedures due to legacy supply chain architecture and conventional delivery processes with poor system compatibility. Consider the following example. It will be very difficult for a logistics manager to track and trace the precise position of a vehicle at any given moment in time if an order management system is not in sync with a last-mile 3PL provider’s system. This results in poor visibility causing delays, incorrect ETAs, route diversions, vehicle idling, increased fuel consumption, and renders deliveries opaque to clients, compounding the last-mile delivery problem.
Curbing the impact of the pandemic: Last-mile delivery has been influenced by the ongoing COVID-19 outbreak, which has thrown traditional logistical tactics into chaos. As a result of social distance constraints, the manner shipments are picked up, delivered, and received has changed. Why not? Contactless delivery has become a typical expectation. It ensures that social divisions are maintained.
Contactless deliveries may appear to be a straightforward method in which an executive just drops off an item at a customer’s door, but this is not the case. Without having to open the door, customers should be told when their deliveries are complete. To accomplish zero contact, cash and card payments must be eliminated. To maintain high levels of safety, customers must also be notified of a person’s and store staff’s most recent body temperatures, as well as a timestamp.
Scaling delivery operations: Businesses are reconsidering how they carry out last-mile delivery operations in light of increased online sales and shipment volume, as well as a need to lower delivery times. Many organizations struggle to find CEOs during hectic business days when their resources are spent. This makes it more difficult to commit to same-day deliveries, which pleases customers.
Increasing Carbon Emissions: Unfortunately, transportation is responsible for more than 20% of global carbon emissions. As environmental consciousness grows, more people are ready to pay a premium for items that are organically organic and constructed of recyclable materials. If carbon-neutral delivery is expected, customers will not be surprised. According to studies, 48% of customers choose carbon-neutral delivery. As a result, organizations must design plans for last-mile delivery and adopt best practices to decrease fuel consumption and the number of kilometers driven.
Alignment with warehouse operations: The rise of eCommerce, as well as the increasing demand for quick order fulfillment, has changed the way merchants look at storage. A rising number of corporations are looking into the idea of urban storage, following in the footsteps of Walmart, Target, and IKEA. The concept is simple: the closer a fulfillment center is near a customer, the easier it is to cut delivery times.
Granular Tracking in Logistics: The fundamental difficulty with last-mile delivery is as follows: Is it possible to trace something down to the granular level? Customers frequently inquire about the status of their orders after they have been placed. Forming a single chain and tracing the location of each cargo until it reaches the client becomes impossible. Swiggy and Zomato, two companies that leverage the last-mile delivery method, have done this. On the other hand, eCommerce is still a work in progress.
Inaccurate details: Many retailers do not provide detailed information on their customers. This is a problem for courier companies since they can’t complete orders on time if they don’t have all of the relevant information. Authorities may also detain the commodities at customs or while they are being transported across state lines.
Cost: Last-mile delivery is one of the factors that contribute to a company’s high fulfillment expenses. For this service, the majority of firms offer an additional cost to their customers. For many people, however, this is not the most feasible option. As a result, budgeting for last-mile delivery, as well as replacing for the additional costs, has become a major challenge. It’s becoming increasingly more difficult when multichannel shopping and same-day delivery join the ecosystem.
Takeaway
Since the delivery landscape is always evolving, with innovations like drone deliveries, delivery robots, and self-driving automobiles on the horizon, these last-mile delivery challenges must be addressed as soon as feasible. They would become popular in the blink of an eye, offering a completely new set of challenges that would be several times more onerous than the current ones.
CargoWise One and Soft Freight Logic has the solutions to optimise your last mile delivery challenges.
Contact us today to for a free consultation on how we can automate your first – last mile delivery challenges.