The news of the Russian-Ukraine war has been trending since it began in early 2022. Countless lives and properties have been lost in the conflict.
Besides the humanitarian crisis the war has caused, there have been disruptions in global supply chains. As if this is not enough, the recent pandemic-triggered lockdown in China has further strained the logistics industry.
Downgrading its earlier prediction in January by 0.8 and 0.2 percentage points, the IMF predicts that the world’s economy will expand by 3.6% in 2022 and 2023. This is a clear drop from the 6.1% growth of 2021 – this can be attributed to the war.
Let’s not even get started on what this will mean for price inflation globally. The supply chain has been fragile since the pandemic, only slowly recovering. In this article, we discuss how the Russian-Ukraine conflict will further threaten the stability of the logistics industry globally.
3 Industries That Are Suffering Major Hits From The Russian-Ukraine War
The multiplying ripple effects of the conflict in Ukraine and Russia are not just felt in these regions. On the contrary, these effects have become ‘seismic waves’ affecting many businesses and countries.
For instance, Russia is among the world’s top natural gas, coal, and oil exporters. However, since the U.S placed a sanction on Russia’s oil, the price of crude oil skyrocketed for the first time in 13 years. With a barrel being almost $130, it was no wonder that some consumers in parts of the U.S. bought gasoline at $5 per gallon.
Despite all these effects, the primary concern of experts is the imminent massive shortages and price inflations. Here are some industries directly affected by the ongoing crisis in Russia and Ukraine.
Agriculture
Besides the dependence on Russia for its energy source, Europe and most countries rely on both Russia and Ukraine for agricultural products. Both countries are major global exporters of fertilizers.
The recent sanctions due to the war mean there will be supply shortages. As a result, economists forecast that the world’s GDP may be negatively affected as the ban continues. In addition, the supply shortages will directly impact crop yields globally.
Data from the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations show that the warring countries produce 25% of the world’s trade in wheat. They are also responsible for 60% of global sunflower oil and 30% of global barley exports.
In 2021, Ukraine exported more than $27 billion in agricultural products globally. Countries like Tanzania, Egypt, Nigeria, Turkey, Kazakhstan, and many others, import their wheat from Russia. According to the UN, the war will most likely disrupt the global food supply chain.
For instance, just weeks after the war began, food prices soared, and the cost of grain increased globally. But, according to experts, this is just the beginning.
Automotive
Another sector that has been affected by the Ukraine-Russia conflict is the automotive industry. Many automobile manufacturers have paused production due to scarce parts and raw materials.
For instance, BMW and Volkswagen had to close some assembly lines in Germany. This is due to the short supply of wiring harnesses produced in Ukraine by Leoni. In addition, Ukraine is one of the world’s largest producers of neon gas which is needed to make semiconductors.
Another example is Michelin, the tire manufacturer. The company announced the closure of some assembly plants in Europe due to logistics issues caused by the war.
Manufacturing Industries
In 2021, Russia produced 10% of the world’s nickel trade, making them the third-largest producer. The International Energy Agency predicts that the demand for nickel in electric vehicles and renewable electricity batteries will expand from 196,000 tons in 2020 to 3,804,000 tons in 2040.
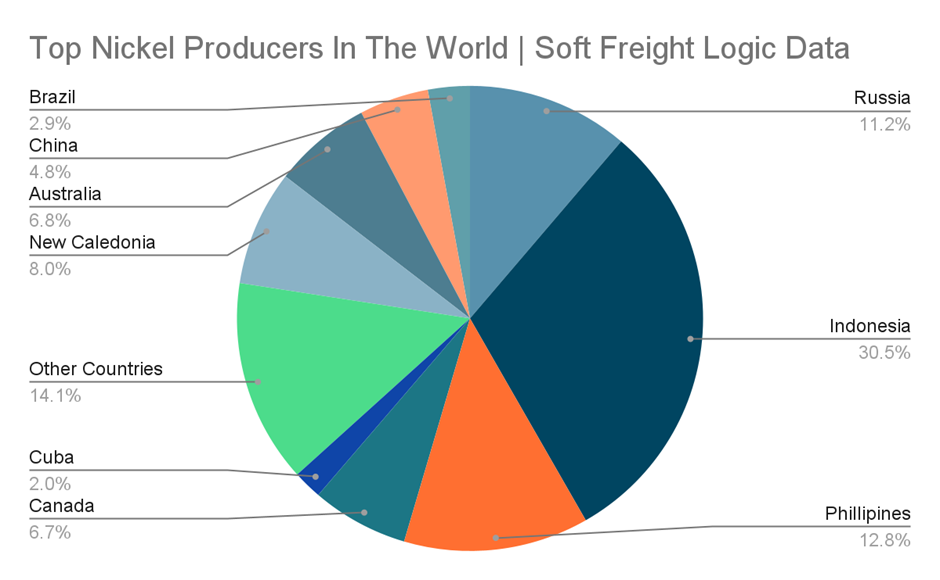
Furthermore, Russia also produces large amounts of steel palladium, platinum, copper, and semi-finished iron and steel products. These products are primarily used by various manufacturing industries globally.
Since the beginning of the war, these raw materials have been scarce. Chips, in particular, have been in short supply across all industries. Also, the electronics industries have taken a significant blow due to these shortages.
Impact Of Russia-Ukraine Conflict On Logistics And Supply Chain
Beyond all these direct and indirect effects on the world’s economy, the Russia-Ukraine crisis is reshaping the global supply chain and shipping routes. For instance, the rising hike in energy sources will most likely increase the cost of transportation.
Most manufacturers and suppliers in Europe, before the war, moved their products and raw materials via rail. However, at this point, there is a need to look towards air and sea freight moving options.
According to some reports, almost 300,000 companies in the U.S. and Europe have suppliers in Russia and Ukraine. Without a doubt, these companies will be forced to look for alternatives to get their raw materials.
Ripple Effects Of The Russian-Ukraine War On The Supply Chain
With the recent developments, industry leaders and Governments are looking for new strategies and alternative sourcing. The goal will be to provide continuous real-time monitoring of all the supply chain tiers.
Here are some of the ways the Ukraine-Russian war will impact the supply chain.
- Logistical routes might need to be rerouted, and alternatives for all Russian imports be sourced.
- Shippers may have to steer clear of the Euro-Asian railway through Russia
- More Dependency on air and sea freight
- Get ready for delays and congestion in deliveries
- Scarcity equals inflation for both producers and consumers
Logistics Industry Trends During The Russian-Ukraine War
Since the war began, the logistics industry has been in shock. We look at some of the global trends in the industry and what it means for business owners.
- There is a 28% decline in the import volume from Russia (Feb 21 – Feb 28). Oil and gas were down by 12%, the manufacturing industry by 56%, and retail sectors by 28% for the same period.
- Since the war began, there has been an increase in delayed shipments to the region. Delayed loads have increased by 20% among LTL loads entering Eastern Europe.
- Export dwell times increased by 25% for all European Ports. While transshipment dwell times increased by 43% (Feb 17 – Mar 2).
- Ocean dwell time in Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG) and Food & Beverage (F&B) increased by 55% (Feb 17 – Mar 2).
- Across Europe, dwell times have been significantly affected. With a 41% increase in Western Europe, 6% in Eastern Europe, 26% in Southern Europe, and 17% in Northern Europe (Feb 17 – Mar 2).
Some Tips To Get Ahead
- Put risk management frameworks in place
- Technology can help you to monitor the risks in each supply chain tier
- Get Alternative and multiple sources of suppliers
- Pay more attention to logistics constraints and costs
- Prioritize Cybersecurity risk monitoring
- Plan for more disruptions in operation in the conflict region
In Conclusion
Despite all these challenges that the logistics industry is facing, a lot can be done to manage the risks. For instance, to fight the scarcity of agricultural products and rising food inflations, Egypt’s prime minister fixed bread prices. In addition, Bangladesh started a food subsidy program.
The Russian-Ukraine war is devastating, and its long-term effects cannot be adequately quantified yet. However, business owners and industry leaders can only hope to create and implement new strategies that will soon help all supply chain operations.